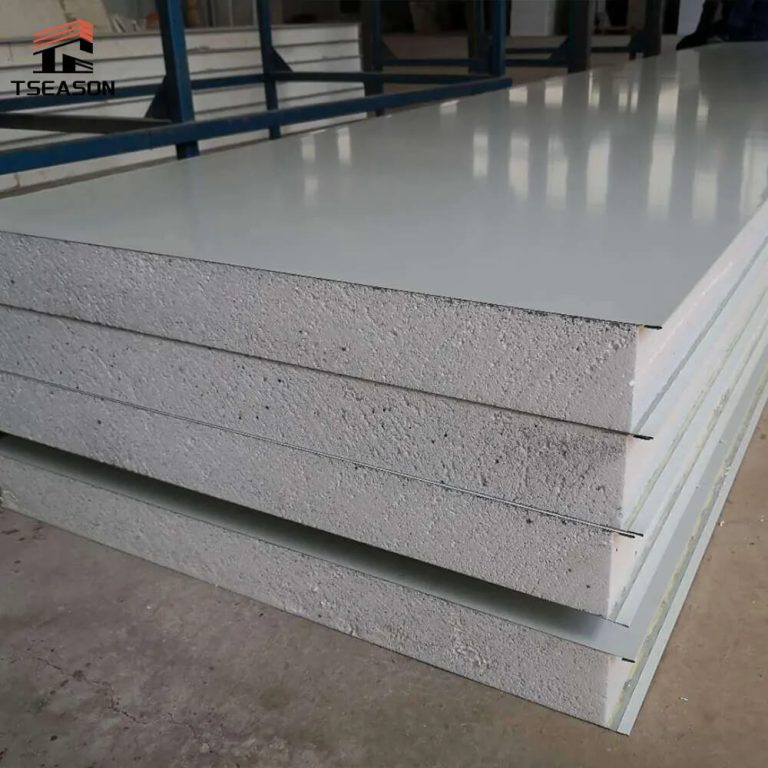
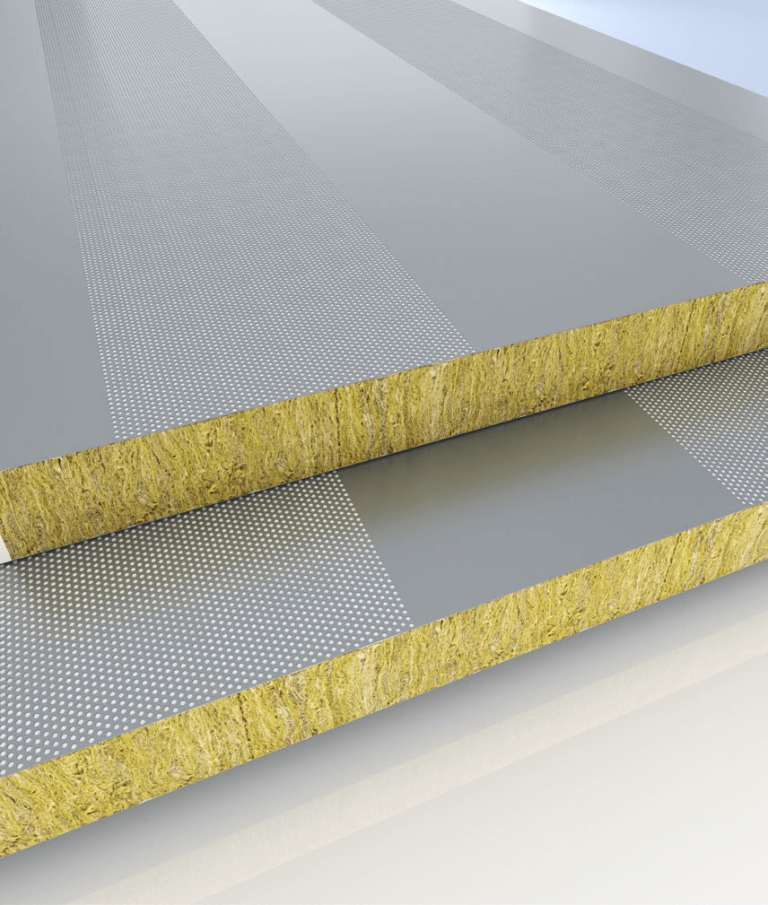
PU Cold Room Panels: Balancing Initial Investment and Long-Term Efficiency Through Material Selection

The PU cold room panels currently play a crucial role in the initial investment cost and long-term benefits of cold storage engineering construction. Although cheap raw materials can reduce initial investment, high-quality raw materials can bring greater long-term returns. Facing fierce competition from raw material suppliers and raw materials whose quality can only be determined after use, making better choices has become a headache for every cold storage investor.
The polyurethane spraying materials used for cold storage thermal insulation generally adopt similar black materials and spraying construction processes among different manufacturers, and the foams produced also appear similar in appearance. However, the difference in white materials used will largely cause performance variations among finished products, and even the use of some inferior white materials may make the original intention of thermal insulation fail to be realized. To enable products to achieve thermal insulation and energy-saving effects and maximize the long-term interests of cold storage investors, the quality control of the company's products is combined here to introduce the following briefly:
1. Thermal Insulation Performance of Cold Storage Insulation Materials
The primary requirement for PU cold room panels used in cold storage is their thermal insulation performance, which cannot be observed with the naked eye before actual use. By the time the difference in power consumption is noticed, it is often too late. The company has conducted extensive experimental testing and strictly controlled material selection to achieve this goal:
- Using structural flame-retardant polyether to reduce thermal conductivity and enhance thermal insulation effects.
- Minimizing the water content in various raw materials and formulas to avoid deterioration of thermal insulation performance caused by water foaming.
- Using high-efficiency and odorless amine catalysts to effectively adjust the balance between foaming-gelation reactions, making the skin between spraying layers thinner, which is conducive to the manifestation of the thermal insulation material performance in cold storage.
- Not using ordinary polyester polyols.
These control measures have achieved remarkable results. Through comparisons of several cold storage facilities, it is evident that those with strict material and construction control have significantly lower power consumption.

2. Dimensional Stability of Polyurethane Insulation Material Foam
The polyurethane foam material in cold storage may experience dimensional changes (generally shrinkage) under drastic temperature changes or long-term low temperatures. Dimensional changes often manifest as foam cracking or detachment, which will inevitably affect the normal use of the cold storage. In addition to regularly conducting simulated performance tests, more attention is paid to material selection control:
- The compound use of special high-functionality polyether enables the foam to form a three-dimensional network structure, greatly improving the low-temperature resistance of the foam. However, the commonly used 4110 polyether in spraying materials contains a large number of difunctional components, and the large number of linear molecular structures formed after the reaction are difficult to stabilize at low temperatures.
- The use of high-functionality crosslinking agents also greatly improves the dimensional stability of the foam.
- The selected polyether adopts strong alkali catalysis in the production stage, with a complete reaction, so that the polyether maintains a high reaction rate (i.e., it can react more completely when in contact with black material). Some manufacturers add open-cell components to the foaming material to prevent apparent deformation of the foam, which reduces the closed-cell rate of the foam and achieves the effect of dimensional stability, but this sacrifices the thermal insulation performance of the pu cold room panels foam.
3. Service Life of Polyurethane Cold Storage Insulation Material Foam
In addition to the initial basic properties of polyurethane foam, the degradation status of the foam is also an important indicator. When formulating white materials, the use of certain polyester materials may make the foam have better toughness and impact resistance on the surface, but after the cold storage is used for a period, it will become brittle and no longer resistant to impact or collision. In addition, the poor hydrolysis resistance of some polyester structural foams will also affect the service life of the foam. The adoption of a polyether structure makes it slightly brittle initially, but the brittleness generally disappears after a few days, and then the stable performance of the cold storage thermal insulation material is maintained for a long time.

4. Suggestions on the Foaming Capacity of Polyurethane Cold Storage Insulation Materials
Cold storage investment is a long-term investment with a return on investment. Although a high foaming capacity can reduce initial investment, it is necessary to grasp a certain limit and comprehensively consider long-term energy consumption and initial investment, because the thermal insulation effect of PU cold room panels has a parabolic correlation with their bulk density. A large number of studies have shown that when the bulk density of the foam is 33~35 kg/m³, it has better thermal insulation performance and service life. Therefore, it is generally recommended that the foaming capacity of constant temperature cold storage be 22~23 m³/ton.
Cautious Suggestion:
The key performance indicators of PU cold room panels, such as thermal insulation performance, dimensional stability, and service life, are invisible, intangible, and imperceptible. The difference between good and bad is only a thin line. When choosing cold storage insulation materials, please first choose "high quality" and then pay attention to "low price". Do not blindly focus on the price!